You are here
Kurikulum Program Studi Sastra Inggris
Primary tabs
KURIKULUM 2025
PROGRAM STUDI SASTRA INGGRIS
Ekuivalensi Kurikulum
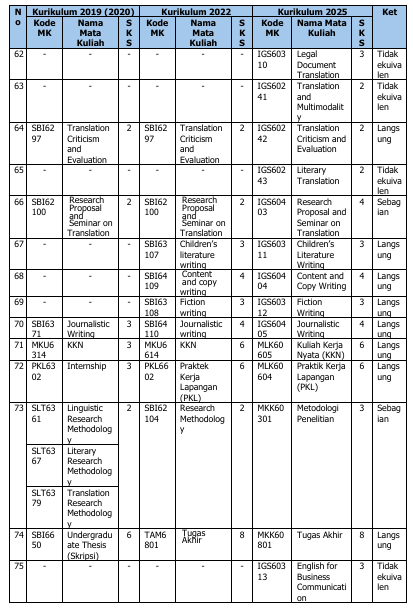
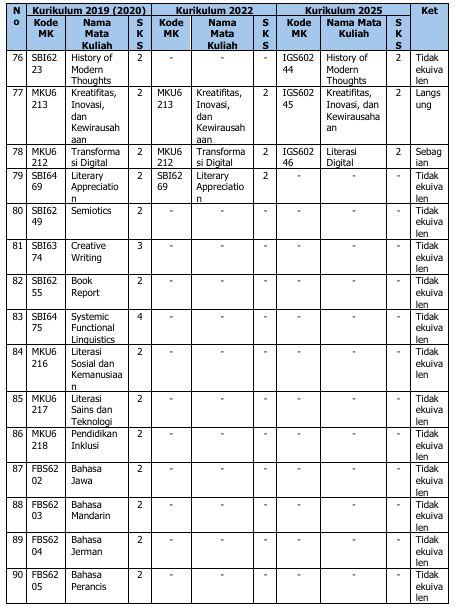
Perubahan kurikulum ini berdampak pada kode dan mata kuliah. Tabel 3 di bawah ini berisimatakuliahyangmengalamiperubahannama, kode, maupunperubahanstatus(dihapus, ditambah, atau diubah jumlah SKSnya).
Tabel 3. Ekuivalensi Kurikulum 2019/2020, 2022, dan 2025
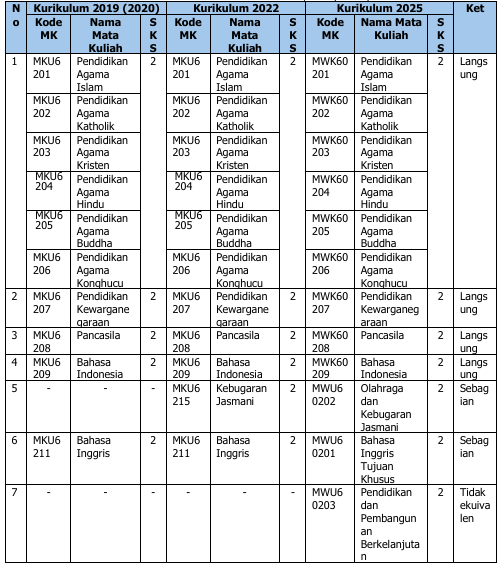
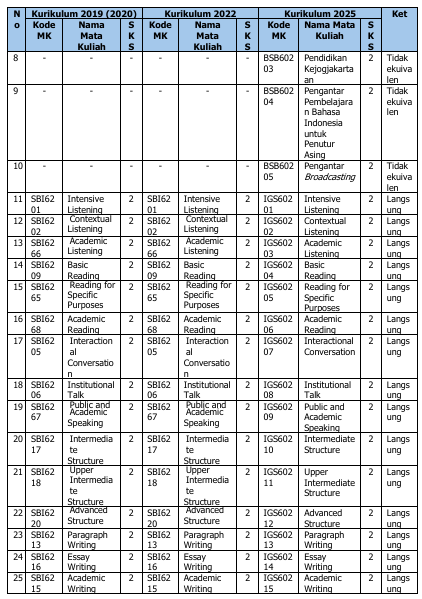
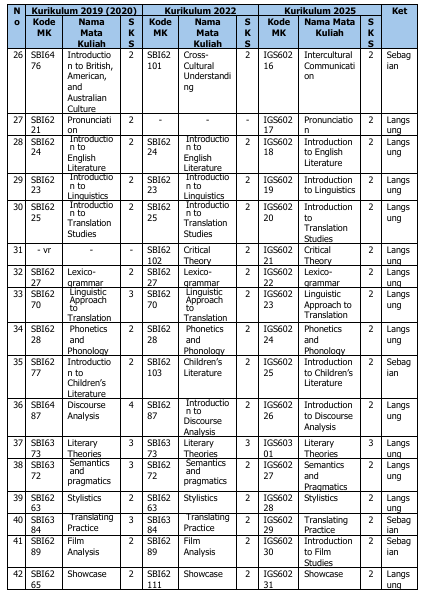
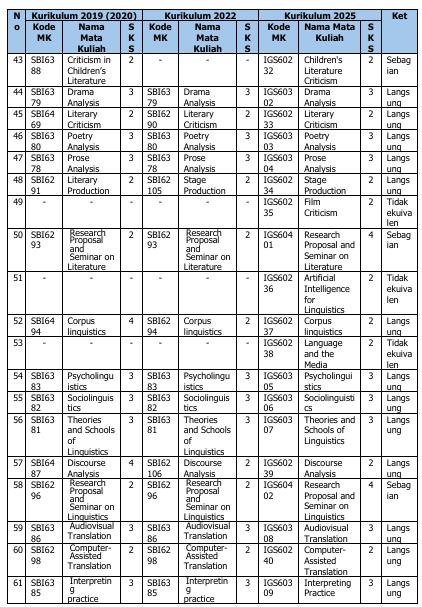
Catatan:
1. Mata kuliah dengan kode IGS60313, IGS60244, IGS60245, dan IGS60246 adalah mata kuliah pilihan prodi.
2. Mata kuliah dengan kode BSB60203, BSB60204, dan BSB60205 adalah mata kuliah pilihan fakultas, mahasiswa bebas memilih untuk mengambil atau tidak selama studi.
3. Mata kuliah paket konsentrasi Literature/Linguistics/Translation: mahasiswa wajib memilih salah satu paket konsentrasi dengan bobot 21 SKS per paket konsentrasi.
4. Mata kuliah dengan kode IGS60232, IGS60302, IGS60233, IGS60303, IGS60304, IGS60234, IGS60235, dan IGS60401 adalah mata kuliah pilihan paket konsentrasi Literature.
5. Mata kuliah dengan kode IGS60236, IGS60237, IGS60238, IGS60305, IGS60306, IGS60307, IGS60239, dan IGS60402 adalah mata kuliah pilihan paket konsentrasi Linguistics.
6. Mata kuliah dengan kode IGS60308, IGS60240, IGS60309, IGS60310, IGS60241, IGS60242, IGS60243, dan IGS60403 adalah mata kuliah pilihan paket konsentrasi Translation.
7. Mata kuliah tambahan kompetensi (MKTK) dengan kode IGS60313, IGS60244, IGS60245, dan IGS60246: mahasiswa memilih minimal 5 sks selama studi.
A. VISI, MISI, DAN TUJUAN PENDIDIKAN PROGRAM STUDI
1. Visi Keilmuan Program Studi Sastra Inggris:
Menjadi program studi unggulan dalam pengembangan kemampuan analisis dan apresiasi kajian bahasa dan sastra Inggris, serta penerjemahan yang berfokus pada pemahaman lintas budaya, serta pengembangan keterampilan komunikasi dan pemecahan masalah berbasis teori sastra, linguistik, dan penerjemahan.
2. Misi Program Studi Sastra Inggris:
a. Menyelenggarakan pendidikan di bidang ilmu bahasa dan sastra Inggris serta penerjemahan yang unggul, kreatif, dan inovatif berkelanjutan berbasis perkembangan ilmu pengetahuan dan teknologi untuk menghasilkan lulusan yang kompeten, tangguh di level nasional dan global, dan memiliki daya saing tinggi dalam keilmuan serta dunia profesional;
b. Menyelenggarakan penelitian, pengembangan, dan penyebarluasan bidang bidang ilmu bahasa dan sastra Inggris, serta penerjemahan yang unggul, kreatif, dan inovatif berkelanjutan, yang berorientasi pada pelestarian dan pengembangan nilai-nilai budaya lokal dan nasional untuk dapat berkontribusi positif bagi masyarakat dan keilmuan, baik di tingkat lokal, nasional, maupun internasional;
c. Menyelenggarakan kegiatan pengabdian kepada masyarakat yang unggul, kreatif, dan inovatif berkelanjutan, yang berorientasi pada penerapan bidang ilmu bahasa dan sastra Inggris, serta penerjemahan untuk memperkaya pemahaman budaya lokal dan nasional, serta meningkatkan kualitas ilmu dan sumber daya di berbagai lapisan masyarakat, baik di tingkat lokal, nasional, maupun internasional;
d. Menyelenggarakan dan membangun jejaring kerja sama dengan dunia pendidikan, dunia usaha dan industri, serta lembaga penelitian yang berkelanjutan di tingkat lokal, nasional, dan internasional untuk mendukung pengembangan bidang ilmu bahasa, sastra, terjemahan, budaya dan penerapannya serta menciptakan peluang bagi mahasiswa dan dosen untuk terlibat dalam berbagai kegiatan pendidikan, penelitian, dan pengabdian kepada masyarakat; dan
e. Menyelenggarakan pelayanan yang optimal kepada mahasiswa dan masyarakat secara transparan dan akuntabel, yang berorientasi pada peningkatan mutu pendidikan, penelitian, dan pengabdian kepada masyarakat yang inovatif berkelanjutan, serta memastikan pelaksanaan penjaminan mutu yang sinergis antara mahasiswa, dosen, dan para pemangku kepentingan untuk menjaga kualitas program studi secara keseluruhan
3. Tujuan Pendidikan Program Studi:
a. Rumusan Tujuan Pendidikan Program Studi (TPP) Sastra Inggris
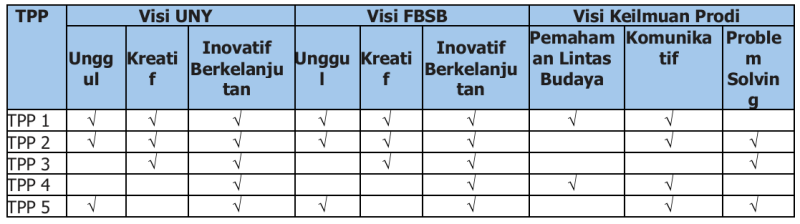
TPP 1 : Menghasilkan lulusan yang unggul, kreatif, inovatif, dan berkelanjutan di bidang ilmu bahasa dan sastra Inggris, serta penerjemahan;
TPP 2 : Menghasilkan penemuan, pengembangan, dan penyebarluasan ilmu pengetahuan dan teknologi di bidang ilmu bahasa dan sastra Inggris, serta penerjemahan yang menyejahterakan individu dan masyarakat, yang mendukung pembangunan daerah dan nasional, serta berkontribusi terhadap pemecahan masalah lokal, nasional, dan global;
TPP 3 : Memberikan kontribusi bagi peningkatan kesejahteraan masyarakat melalui kegiatan pengabdian dan pemberdayaan berbasis bidang ilmu bahasa dan sastra Inggris, serta penerjemahan;
TPP 4 : Memiliki jejaring yang melibatkan masyarakat, akademik, industri, dan media di tingkat lokal, nasional, maupun internasional dalam bidang ilmu bahasa dan sastra Inggris, serta penerjemahan; dan
TPP 5 : Memiliki kualitas pelayanan yang optimal kepada mahasiswa dan masyarakat secara transparan dan akuntabel, yang berorientasi pada peningkatan mutu pendidikan, penelitian, dan pengabdian kepada masyarakat yang inovatif berkelanjutan.
b. Kesesuaian Tujuan Pendidikan Program Studi dengan Visi Perguruan Tinggi, Fakultas, dan Program Studi.
Tabel berikut dapat digunakan untuk memastikan kesesuaian antara TPP dengan visi perguruan tinggi, fakultas, maupun program studi.
Tabel 4. Matriks Kesesuaian TPP dengan Visi Perguruan Tinggi, Fakultas, dan Program Studi
B. PROFIL LULUSAN
1. Profil Lulusan dan Deskripsi Profil
Profil lulusan Program StudiSastra Inggris, Fakultas Bahasa dan Seni, Universitas Negeri Yogyakarta adalah lulusan yang mempunyai kompetensi dasar bahasa Inggris (English Proficiency: ITP TOEFL minimal 500 atau tes jenis lainnya yang setara) yang menghasilkan profesi sebagai:
Tabel 6. Profil Lulusan dan Deskripsi Profil

2. Keselarasan Profil Lulusan dengan Tujuan Pendidikan Program Studi
Untuk memastikan kesesuaian antara profil lulusan dengan tujuan pendidikan program studi dapat dilakukan melalui matrik atau tabel kesesuaian profil lulusan dengan TPP sebagai berikut.
Tabel 7. Kesesuaian Profil Lulusan dengan Tujuan Pendidikan Program Studi Sastra Inggris UNY

C. CAPAIAN PEMBELAJARAN LULUSAN
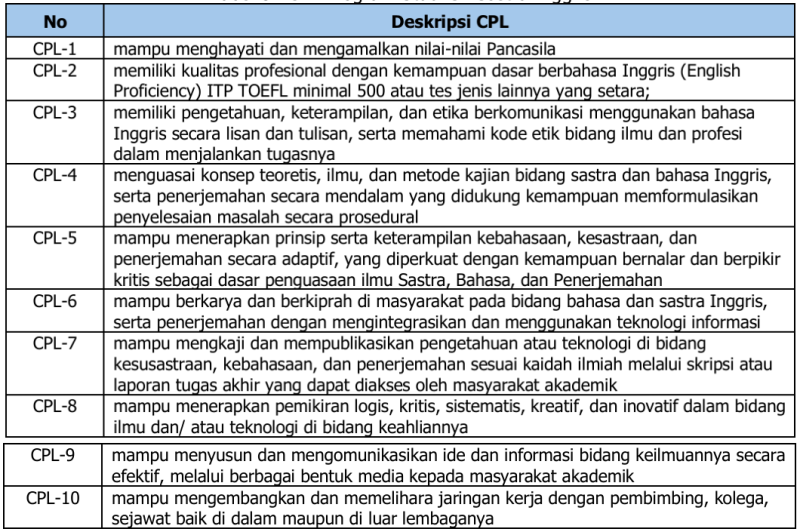
1. Rumusan Capaian Pembelajaran Lulusan (CPL)
Lulusan Prodi Sastra Inggris, Fakultas Bahasa, Seni, dan Budaya, Universitas Negeri Yogyakarta diharapkan:
Tabel 8. CPL Program Studi S1 Sastra Inggris
D. STRUKTUR KURIKULUM DAN SEBARAN MATA KULIAH
1. Struktur Kurikulum
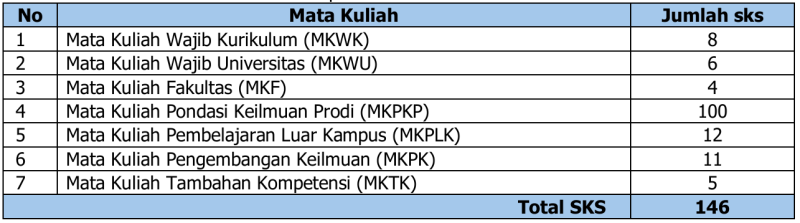
Kurikulum Program Studi Sastra Inggris dirancang dengan beban belajar sejumlah 146 sks dan masa tempuh kurikulum 8 semester, dengan rincian kelompok mata kuliah sebagai berikut.
Tabel 17. Kelompok Mata Kuliah dan Besaran SKS
Catatan:
a. Mata Kuliah Wajib Kurikulum (MKWK) dan Mata Kuliah Wajib Universitas (MKWU) adalah mata kuliah umum untuk pengembangan karakter dan keindonesiaan untuk mencapai visi misi UNY.
b. Mata Kuliah Fakultas (MKF) merupakan mata kuliah penciri Fakultas Bahasa, Seni, dan Budaya.
c. Mata Kuliah Pondasi Keilmuan Prodi (MKPKP) merupakan mata kuliah yang sesuai dengan bidang keilmuan Program Studi Sastra Inggris yang linier dengan profesi penguasaan bidang Literature, Linguistics, dan Translation.
d. Mata Kuliah Pembelajaran Luar Kampus (MKPLK) merupakan kegiatan yang dilaksanakan di luar lingkungan kampus yaitu KKN dan PKL.
e. Mata Kuliah Pengembangan Keilmuan (MKPK) merupakan mata kuliah terkait perkembangan ilmu pengetahuan pada Program Studi Sastra Inggris.
f. Mata Kuliah Tambahan Kompetensi (MKTK) merupakan keterampilan tambahan di luar kurikulum utama program studi Sastra Inggris.
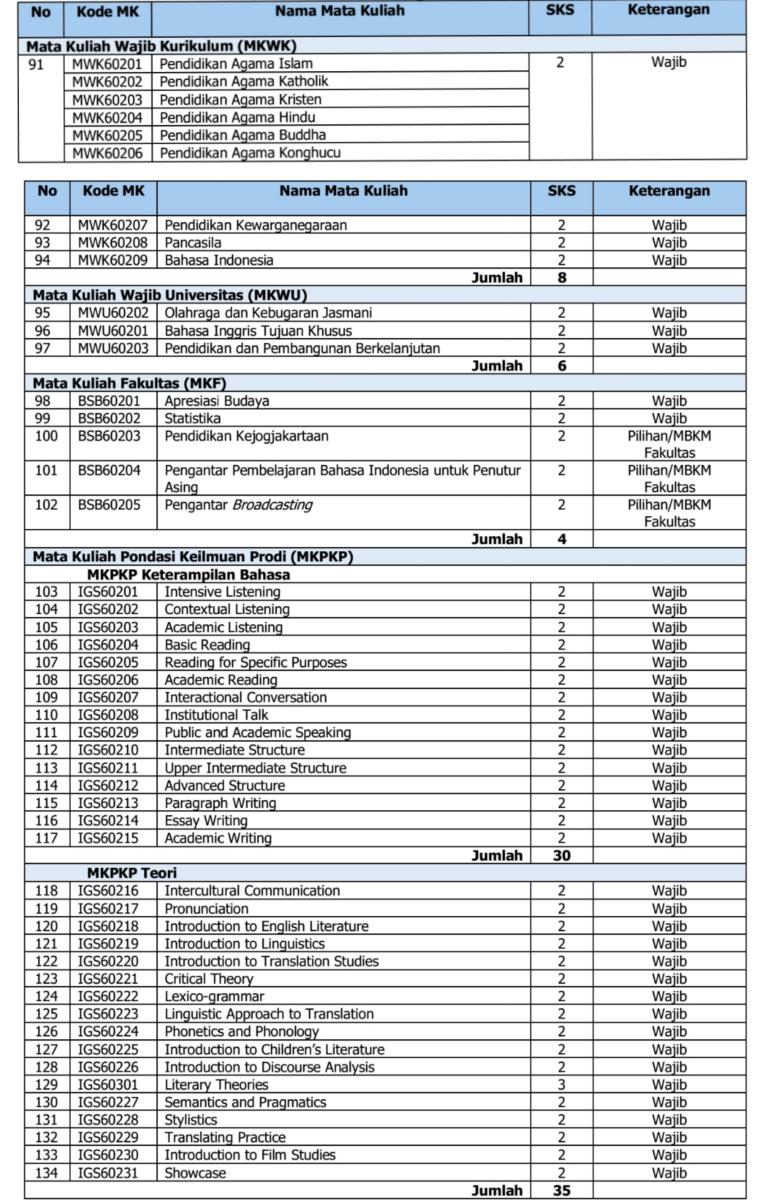
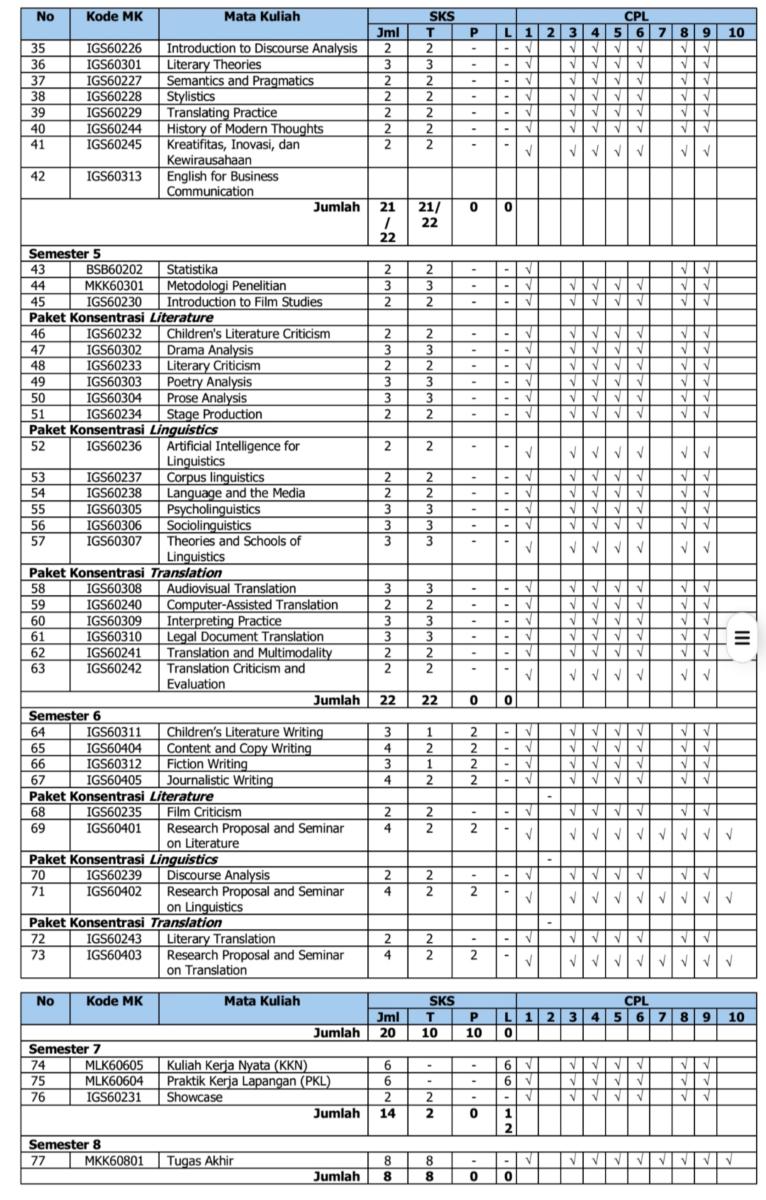
Rincian setiap mata kuliah dalam 7 kelompok mata kuliah dan besaran SKS masing-masing mata kuliah disajikan dalam tabel berikut:
Tabel 18. Daftar Mata Kuliah Program Studi Sastra Inggris

Catatan:
1. Mata kuliah dengan kode IGS60313, IGS60244, IGS60245, dan IGS60246 adalah mata kuliah pilihan prodi.
2. Mata kuliah dengan kode BSB60203, BSB60204, dan BSB60205 adalah mata kuliah pilihan fakultas, mahasiswa bebas memilih untuk mengambil atau tidak selama studi.
3. Mata kuliah paket konsentrasi Literature/Linguistics/Translation: mahasiswa wajib memilih salah satu paket konsentrasi dengan bobot 21 SKS per paket konsentrasi.
4. Mata kuliah dengan kode IGS60232, IGS60302, IGS60233, IGS60303, IGS60304, IGS60234, IGS60235, dan IGS60401 adalah mata kuliah pilihan paket konsentrasi Literature.
5. Mata kuliah dengan kode IGS60236, IGS60237, IGS60238, IGS60305, IGS60306, IGS60307, IGS60239, dan IGS60402 adalah mata kuliah pilihan paket konsentrasi Linguistics.
6. Mata kuliah dengan kode IGS60308, IGS60240, IGS60309, IGS60310, IGS60241, IGS60242, IGS60243, dan IGS60403 adalah mata kuliah pilihan paket konsentrasi Translation.
7. Mata kuliah tambahan kompetensi (MKTK) dengan kode IGS60313, IGS60244, IGS60245, dan IGS60246: mahasiswa memilih minimal 5 sks selama studi.
Berikut adalah penyajian organisasi mata kuliah dalam struktur kurikulum.
Tabel 19. Kelompok Mata Kuliah, CPL, dan Sebarannya dalam Kurikulum

Organisasi mata kuliah dalam struktur kurikulum perlu dilakukan secara cermat dan sistematik untuk memastikan tahapan belajar mahasiswa telah sesuai, menjamin pembelajaran terselenggara secara efisien dan efektif untuk mencapai CPL Program Studi Sastra Inggris. Organisasi mata kuliah dalam struktur kurikulum terdiri dari organisasi horisontal dan organisasi vertikal. Organisasi mata kuliah horisontal dalam semester dimaksudkan untuk perluasan wacanadanketerampilanmahasiswadalamkonteksyanglebihluas, sedangkanorganisasimata kuliah secara vertikal dalam jenjang semester dimaksudkan untuk penguasaan kemampuan sesuai dengan tingkat kesulitan belajar untuk mencapai CPL Program Studi Sastra Inggris yang telah ditetapkan.

Gambar 1. Organisasi Mata Kuliah dalam Kurikulum
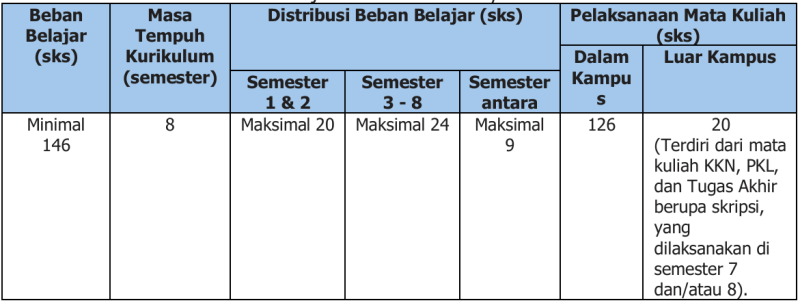
Tabel 20. Beban Belajar dan Pelaksanaannya dalam Kurikulum
2. Sebaran Mata Kuliah
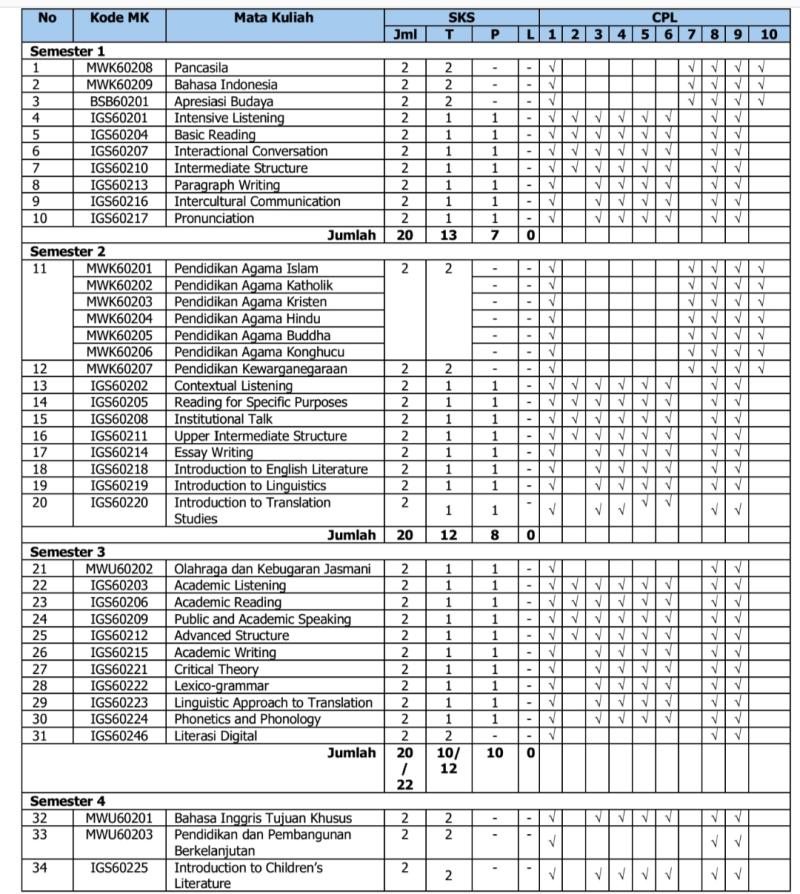
Untuk memudahkan dalam implementasinya, struktur kurikulum perlu disajikan dalam distribusi mata kuliah setiap semester. Berikut adalah contoh penyajian distribusi mata kuliah setiap semester.
Tabel 21. Sebaran Mata Kuliah Program Studi Sastra Inggris -S1
Catatan:
a. Semester 1 dan 2 mahasiswa mengambil beban studi maksimal 20 sks per semester.
b. Semester selanjutnya mahasiswa mengambil beban studi berdasarkan IPK, maksimal 24 sks. c. Semester antara, mahasiswa dapat mengambil maksimal 9 sks.
d. Masa studi maksimal sebesar dua kali masa tempuh kurikulum.
E. PROSES PEMBELAJARAN
Proses pembelajaran di Program Studi Sastra Inggris dilakukan dengan mengacu Standar Nasional Pendidikan Tinggi yang mencakup karakteristik proses pembelajaran, perencanaan proses pembelajaran, pelaksanaan proses pembelajaran; dan beban belajar mahasiswa. Karakteristik proses pembelajaran mencakup sifat interaktif, holistik, integratif, saintifik, kontekstual, tematik, efektif, kolaboratif, dan berpusat kepada mahasiswa. Perencanaan proses pembelajaran disusun untuk setiap mata kuliah dan disajikan dalam rencana pembelajaran semester (RPS) yang dikembangkan oleh dosen secara mandiri atau bersama dalam satu kelompok bidang keahlian.
Pelaksanaan proses pembelajaran berlangsung dalam bentuk interaksi antara dosen, mahasiswa, dan sumber belajar dalam lingkungan belajar tertentu. Pelaksanaan proses pembelajaran dilakukan dengan menggunakan beragam metode pembelajaran: diskusi kelompok, simulasi, studi kasus, pembelajaran kolaboratif, pembelajaran kooperatif, pembelajaranberbasisproyek, pembelajaranberbasismasalah, ataumetodepembelajaranlain, yang dapat secara efektif memfasilitasi pemenuhan capaian pembelajaran lulusan. Setiap mata kuliah dapat menggunakan satu atau gabungan dari beberapa metode pembelajaran dan diwadahi dalam suatu bentuk pembelajaran berupa: (1) kuliah, (2) responsi dan tutorial, (3) seminar, (4) praktikum atau praktik lapangan, (5) magang, (6) penelitian, (7) proyek kemanusiaan, (8) wirausaha, (9) pertukaran pelajar, dan/atau (10) bentuk lain pengabdian kepada masyarakat. Bentuk-bentuk pembelajaran tersebut mengakomodasi minat dan potensi mahasiswa untuk mengembangkan diri sebagai bagian dari kemerdekaan belajar untuk mencapai capaian pembelajaran yang diinginkan.
Pembelajaran di Program Studi Sastra Inggris telah memanfaatkan kemajuan teknologi. Beberapa mata kuliah telah mengembangkan perkuliahan daring yang dapat digunakan secara penuh maupun blended learning dan dapat diakses melalui Learning Management System (BeSmart UNY) di laman https://besmart.uny.ac.id/v2/. Mahasiswa juga dituntut untuk dapat memanfaatkan teknologi melalui berbagai aplikasi yang tersedia.
Beban belajar mahasiswa dinyatakan dalam besaran satuan kredit semester (sks). Satu sks kegiatan kuliah setara dengan 45 jam per semester. Hal ini setara dengan 170 (seratus tujuh puluh menit: 50 menit tatap muka, 60 menit tugas terstruktur, dan 60 menit kegiatan mandiri) kegiatan belajar per minggu per semester. Setiap mata kuliah paling sedikit memiliki bobot 1 (satu) sks. Semester merupakan satuan waktu kegiatan pembelajaran efektif selama 16 (enam belas) minggu.
Prosespembelajaranditujukanuntuk memenuhicapaiankompetensiprogramstudisesuai dengan capaian pembelajaran lulusan maupun capaian pembelajaran mata kuliah. Capaian kompetensi tersebut menuntut diselenggarakannya proses pembelajaran dengan sistem yang terpusatpadamahasiswa(studentlearningcenter). Pembelajaranmenekankanpadapenguatan kompetensi kepribadian, sosial, pedagogis dan profesional.
Pembelajaran dapat dilaksanakan dengan sistem tatap muka/pertemuan, termasuk e-learning penugasan terstruktur, tugas mandiri dan kegiatan lain yang ekuivalen, seminar, praktik dan penelitian serta pengabdian pada masyarakat. Pembelajaran juga dapat dilakukan dengan blended learning atau model e-learning penuh. Pembelajaran secara keseluruhan berjumlah 16 kali pertemuan per semester. Mahasiswa wajib hadir mengikuti perkuliahan minimal 75% dari tatap muka yang terselenggara.
Pelaksanaan pembelajaran pada prinsipnya menyangkut tiga tahap: tahap pendahuluan, kegiatan inti/penyajian, dan penutup. Terkait dengan prinsip belajar tuntas, maka kegiatan pembelajaran merupakan proses fasilitasi mahasiswa untuk memperoleh pengalaman belajar dan ketuntasan sesuai dengan capaian kompetensi yang telah ditentukan. Oleh karena itu pendekatan kontekstual dengan kegiatan yang mendorong mahasiswa aktif, inovatif, kreatif, inspiratif, dan membangun suasana yang menyenangkan, menjadi proses pembelajaran yang terus dikembangkan. Perspektif karakter, nilai-nilai kebangsaan dan jiwa kewirausahaan menjadi bagian tidak terpisahan dalam membangun makna pembelajaran. Melalui proses pembelajaran yang dikembangkan, keberhasilan mahasiswa ditentukan tidak hanya berdasarkan hardskills, kemampuan intelektual (indeks prestasi), tetapi juga softskills dengan melihat kemampuan kognitif, karakter, kepribadian dan moralitas.
F. PENILAIAN
Penilaian pembelajaran merupakan bagian penting dari kurikulum untuk melihat keberhasilan mahasiswa dalam menuntaskan capaian pembelajaran yang telah ditentukan. Sesuai dengan Permendikbud Nomor 53 Tahun 2023 tentang Sistim Penjaminan Mutu Pendidikan Tinggi terkait standar penilaian pembelajaran, Program Studi Sastra Inggris. melaksanakan proses penilaian berdasarkan prinsip edukatif, otentik, objektif, akuntabel, dan transparan. Penilaianpembelajaranmeliputiduaaspek yaitupenilaianprosesdanpenilaian hasil pembelajaran. Penilaianprosesdigunakanuntuk mendapatkanpemahamantentang bagaimana mahasiswa terlibat dalam proses perkuliahan termasuk di dalamnya aspek kepribadian dan karakter. Penilaian hasil ditunjukkan untuk mendapatkan gambaran capaian kompetensi (ketuntasan CPL) setelah mengikuti proses pembelajaran.
Penilaian proses digunakan untuk melihat keterlibatan mahasiswa dalam perkuliahan meliputi aspek softskills dalam hal partisipasi dalam kegiatan perkuliahan, kemampuan mengartikulasikan gagasan, menggugah tanggungjawab dan kemandirian, memunculkan jiwa solidaritas dan kemampuan kerjasama, dan mendorong peningkatan motivasi mahasiswa. Penilaian proses dilakukan dengan metode pengamatan, penilaian teman sejawat, dan portofolio. Penilaian ini dilakukan selama proses perkuliahan sebagai salah satu komponen yang menentukan nilai akhir.
Penilaian hasil digunakan untuk menilai kemampuan mahasiswa dalam mencapai kompetensi yang menjadi capaian pembelajaran. Penilaian hasil dilakukan melalui uji kompetensi setiap sub kompetensi atau SubCPMK yang diajarkan, ujian tengah semester, ujian praktik, ujian akhir semester. Metode penilaian hasil dilakukan dengan ujian tertulis, penulisan esai/makalah, ujian lisan, ujian praktik maupun portofolio.
Berbagai Teknik penilaian dapat dilakukan antara lain observasi, partisipasi, unjuk kerja, tes tertulis, tes lisan, dan angket. Instrumen penilaian proses pembelajaran dapat berupa rubrik dan /atau penilaian hasil dalam bentuk portofolio. Hasil akhir penilaian merupakan integrasi antara berbagai teknik dan instrumen penilaian yang digunakan.
Pengukuran dan penilaian perlu semaksimal mungkin menyasar pada seluruh domain kemampuan yang dikembangkan dalam masing-masing mata kuliah, baik berupa pengetahuan, sikap, dan keterampilan. Penilaian dilakukan melalui berbagai cara, baik tes maupun non-tes sehingga hasilnya otentik dan sesuai jenis kemampuan atau capaian pembelajaran mata kuliah, termasuk kemungkinannya melakukan penilaian non-tes yang mencakup 4P (Performansi, Produk, Proyek, dan Portofolio). Sesuai SN-Dikti, pengukuran/penilaian pada semua jenjang pendidikan tinggi harus memperhatikan aspek-aspek validitas, reliabilitas, komprehensif, aspek karakter, dan berkelanjutan.
Pelaporan penilaian berupa kualifikasi keberhasilan mahasiswa dalam menempuh suatu mata kuliah yang dinyatakan dalamkisaran angka dan hurufsesuai dengan peraturan akademik yang berlaku. Mahasiswa berprestasi akademik tinggi adalah mahasiswa yang mempunyai indeks prestasi semester (IPS) lebih besar dari 3,50 (tiga koma lima nol) dan memenuhi etika akademik.
G. DESKRIPSI MATA KULIAH
1. PendidikanAgama
a. PendidikanAgamaIslam(MWK60201)
Mata kuliah PAI bertujuan untuk memperkuat iman dan takwa kepada Allah Swt. serta memiliki akhlak (karakter) mulia serta memperluas wawasan keilmuan dan hidup beragamanya, sehingga terbentuk mahasiswa Muslim yang berbudi pekerti luhur, berpikir filosofis, bersikap rasional dan dinamis, serta berpandangan luas, dengan memperhatikan tuntutan untuk menjalin harmoni antarsesama manusia baik dalam satu umat beragama maupun dengan umat beragama lain.
b. PendidikanAgamaKatholik(MWK60202)
Mata kuliah Pendidikan Agama Katolik bersifat wajib lulus bagi setiap mahasiswa yang beragama Katolik di semua program studi, berbobot 3 SKS. Mata kuliah ini dirancang dengan maksud untuk memperkuat iman dan taqwa kepada Tuhan Yang Maha Esa, serta memperluas wawasan hidup beragama, sehingga terbentuk mahasiswa yang berbudi pekerti luhur, berpikir filosofis, bersikap rasional dan dinamis dan berpandangan luas, dengan memperhatikan tuntutan untuk menghormati intra dalam satu umat, dan dalam hubungan kerukunan antarumat beragama. Kegiat- an perkuliahan dilakukan dengan model ceramah, dialog, dan presentasi makalah. Evaluasi dilakukan melalui tertulis, tugas, dan laporan, serta presentasi.
c. PendidikanAgamaKristen(MWK60203)
Mata kuliah Pendidikan Agama Kristen bersifat wajib lulus bagi setiap mahasiswa yang beragama Kristen di semua program studi, berbobot 3 SKS. Mata kuliah ini dirancang dengan maksud untuk memperkuat iman dan taqwa kepada Tuhan Yang Maha Esa, serta memperluas wawasan hidup beragama, sehingga terbentuk mahasiswa yang berbudi pekerti luhur, berpikir filosofis, bersikap rasional dan dinamis dan berpandangan luas, dengan memperhatikan tuntutan untuk menghormati intra dalam satu umat, dan dalam hubungan kerukunan antarumat beragama. Kegiatan perkuliahan dilakukan dengan model ceramah, dialog, dan presentasi makalah. Evaluasi dilakukan melalui tertertulis, tugas, dan laporan, serta presentasi.
d. PendidikanAgamaHindu(MWK60204)
Agama seperti yang dipahami oleh kebanyakan orang Hindu bukanlah teori yang harus dihapal, bukan pula dogma semata dan bukan pula kata- kata yang hampa makna. Agama adalah tuntutan yang mengandung seperangkat nilai yang jika diamalkan akan sangat berguna bagi dirinya dan bagi orang lain. Mata kuliah Pendidikan Agama Hindu bersifat wajib lulus bagi setiap mahasiswa yang beragama Hindu di semua program studi, berbobot 3 SKS. Matakuliah ini dirancang dengan maksud untuk memperkuat iman dan taqwa kepada Tuhan Yang Maha Esa, serta memperluas wawasan hidup beragama, sehingga terbentuk mahasiswa yang berbudi pekerti luhur, berpikir filosofis, bersikap rasional dan dinamis dan berpandangan luas, dengan memperhatikan tuntutan untuk menghormati intra dalam satu umat, dan dalam hubungan kerukunan antarumat beragama. Kegiatan perkuliahan dilakukan dengan model ceramah, dialog, dan presentasi makalah. Evaluasi dilakukan melalui tes tertulis, tugas, dan laporan, serta presentasi. Mata kuliah ini berisi pokok bahasan: (1) mengenal agama; (2)sradda; (3) marga menuju tuhan; (4) tata susila; (5)kebutuhanhiduporanghindu;(6)hidupberkeluarga;(7)ilmupengetahuandanagama; (8) yajna: komunikasi simbolik; (9) kerjasama antar umat beragama; (10) pelayanan sebagai pemujaan.
e. PendidikanAgamaBuddha(MWK60205)
Mata kuliah Pendidikan Agama Budha bersifat wajib lulus bagi setiap mahasiswa yang beragama Budha di semua program studi, berbobot 3 SKS. Mata kuliah ini dirancang dengan maksud untuk memperkuat iman dan taqwa kepada Tuhan Yang Maha Esa, serta memperluas wawasan hidup beragama sehingga terbentuk mahasiswa yang berbudi pekerti luhur, berpikir filosofis, bersikap rasional dan dinamis dan berpandangan luas, dengan memperhatikan tuntutan untuk menghormati intra dalam satu umat, dan dalam hubungan kerukunan antarumat beragama. Kegiatan perkuliahan dilakukan dengan model ceramah, dialog, dan pre- sentasi makalah. Evaluasi dilakukan melalui tes tertulis, tugas, dan laporan, serta presentasi.
f. PendidikanAgamaKonghucu(MWK60206)
Mata kuliah PendidikanAgama Konghucu bersifat wajib lulus, berbobot 3 SKS. Mata kuliah ini dirancang untuk memperkuat iman dan taqwakepadaTuhanYME, sertamemperluas wawasan hidup beragama, sehingga terbentuk mahasiswa yang berbudi pekerti luhur, berpikir filosofis, rasional dan dinamis serta berpandangan luas. Kegiatan perkuliahan dilakukan dengan model ceramah, dialog, dan presentasi makalah. Evaluasi dilakukan melalui tes tertulis, penugasan dan laporan serta presentasi.
2. PendidikanKewarganegaraan(MWK60207)
Mata kuliah Pendidikan Kewarganegaraan bersifat wajib lulus, berbobot 2 SKS. Mata kuliah ini membekali peserta didik dengan pengetahuan dan kemampuan dasar berkenaan dengan hubungan antara warga negara dengan negara,serta pendidikan pendahuluan bela negara agar menjadi waga negara yang dapat diandalkan oleh bangsa dan negaranya. Mata kuliah ini mengkaji : (1) Hak dan kewajiban warga negara; (2) Pendidikan pendahuluan bela negara (3) Demokrasi Indonesia; (4) Hak asasi manusia; (5) Wawasan Nusantara dan identitas nasional Indonesia; (6) Ketahanan nasionional Indonesia; serta strategi ketahanan nasional Indonesia.
3. Pancasila(MWK60208)
Perkuliahan ini membahas tentang landasan dan tujuan Pancasila, Pancasila sebagai hasil berpikir ilmiah, Pancasila dalam konteks sebagai perjuangan bangsa Indonesia, Pancasila sebagai sistem nilai dan ideology nasional, UUD dan Amandemennya serta Pancasila sebagai paradigma kehidupan bermasyarakat, berbangsa, dan bernegara.
4. BahasaIndonesia(MWK60209)
MatakuliahBahasaIndonesiainiberbobot2 sks wajiblulusdengannilaiminimalC. Tujuan, membekali mahasiswa kompetensi membuat artikel/laporan kegiatan ilmiah menggunakan Bahasa Indonesia secara benar. Isi kuliah mencakup deskripsi, contoh dan latihan membuat: 1) kalimat tunggal yang terdiri atas Subyek, Predikat, dan Obyek (SPO); 2) kalimatganda;3)kalimatyangmemuatpokokpikiran(kalimatpokok);4)mengembangkan kalimat pokok menjadi paragraph sederhana yang terdiri atas: kalimat kokok, kalimat pendukung, dan kalimat penjelas; 5) paragraph yang terdiri atas kalimat: pengantar, pokok, pendukung, penjelas, dan kesimpulan; 6) artikel pendek yang memuat satu pokok pikirandanterdiriatasparagraph: pengantar, isi/pokok, dankesimpulan;7)artikelpanjang yang memuat satu kendali gagasan yang dijabarkan menjadi dua atau lebih pokok pikiran dan disusun menjadi paragraph padu dan berdasarkan data, secara struktue terdiri atas paragrap: pengantar, isi/pokok, dan kesimpulan; serta menggunakan kata sambung, transisi; dan sinonim.
5. OlahragadanKebugaranJasmani(MWU60202)
Mata kuliah kebugaran jasmani merupakan mata kuliah wajib tempuh dengan bobot 2 SKS teori. Mata kuliah ini mengkaji konsep kebugaran jasmani, dasar-dasar latihan kebugaran jasmani, metode latihan kebugaran jasmani, pengembangan program latihan kebugaran jasmani, praktek program olahraga untuk meningkatkan kebugaran jasmani dan program kebugaran jasmani berbasis rekreasi.
6. BahasaInggrisTujuanKhusus(MWU60201)
This course is a compulsory subject which is designed to introduce students to English proficiency tests. It is to measure their proficiency in using and understanding English as a foreignlanguageforacademicpurposes. Itintroducesthemto the threeEnglishproficiency skills, i.e. listening skills, grammar and reading skills. Lecturing will be the technique in delivering the materials and students are assigned to do structured works both in the classroom and at home. Students’ learning will be assessed through classroom performance, assignments, mid test as well as final test.
7. PendidikandanPembangunanBerkelanjutan(MWU60203)
8. ApresiasiBudaya(BSB60201)
Mata kuliah ini bertujuan untuk memberikan kompetensi kepada mahasiswa untuk dapat mengapresiasi dan mengkritisi konsep, wujud, unsur, sifat dan perubahan budaya, sehingga tercipta situasi sadar budaya untuk membangun ketahanan budaya yang tangguh. Materi pembelajaran meliputi konsep apresiasi, tingkat-tingkat apresiasi, konsep budaya, Wujud Budaya, Unsur Budaya, sifat budaya, peran budaya, perubahan budaya, unsur kemanusiaan, serta fenomena budaya. Kegiatan belajar mengajar dilaksanakan dengan diskusi, praktik apresiasi, dan pengamatan lapangan. Evaluasi dilakukan melalui presentasi, hasil tes, tugas kelompok dan mandiri. Kegiatan pembelajaran dilaksanakan dengan ceramah, diskusi, praktik apresiasi, studi lapangan, dan pengkritisan atas fenomena-fenomena budaya.
9. Statistika(BSB60202)
Mata kuliah ini bertujuan memberi bekal kompetensi kepada mahasiswa untuk memanfaatkan teknik-teknik analisis statistik dalam penelitian pembelajaran Bahasa Inggris. Bahan kuliah meliputi dasar-dasar statistik, jenis-jenis skala pengukuran, statistik deskriptif, dan pengujian hipotesis. Kegiatan perkuliahan dilaksanakan melalui kuliah di dalam kelas, diskusi, praktik pemanfaatan program komputer untuk melakukan analisis statistik, dan tugas individu. Penilaian dilakukan dengan mempertimbangkan kehadiran dalam perkuliahan, keaktifan dalam kegiatan perkuliahan, tugas individu, dan hasil ujian akhir semester.
10.PendidikanKejogjakartaan(BSB60203)
11.PengantarPembelajaranBahasaIndonesiauntukPenuturAsing(BSB60204)
12.PengantarBroadcasting(BSB60205)
13.IntensiveListening(IGS60201)
This subject provides students with basic skills in comprehending simple oral discourses through the recorded voice of native speakers. Material is presented in a variety of short functional texts with exercises covering sound recognition and discrimination as well as stresses andintonation and their meanings. Students’ classroom activities include individual work, pair work, and group work. Evaluation of students’ achievement is based on classroom participation, home assignments, quizzes, and the final test.
14.ContextualListening(IGS60202)
This subject provides students with pre-intermediate to intermediate skills in comprehending simple oral discourses through the recorded voice of native speakers or non-native speakers in English. Materials are presented in a variety of short functional texts with exercises focused on answering questions, both factual and inferential in nature, following a given text and making inferences from it. Students’ classroom activities include individual work, pair work, group work, and presentation. Evaluation of students’ achievement is based on classroom participation, class/home assignments, and/or the final test.
15.AcademicListening(IGS60203)
This subject provides students with intermediate to upper-intermediate skills in comprehending oral discourses through the recorded voices of native speakers. Materials are presented in a variety of functional texts with exercises focused on extracting specific information from a given text and giving details of it. Students’ classroom activities include individual work, pair work, and group work. Evaluation of students’ achievement is based on classroom participation, class and home assignments, and the final test.
16.BasicReading(IGS60204)
While developing the basic competencies of reading initiated at secondary schools (such as getting general and specific information from the text, getting the main ideas and detailed information from the text, deducing the meaning of words, phrases and sentences based on the context, and explaining relations between parts of the text through grammatical cohesive devices), the course develops the skills ofscanning, skimming, making inferences, summarizing, andspeed-reading. Inorderto aidthelanguagedevelopment, authentictexts of general topics are used. While individual performances are noted, pair and group works should be encouraged. Assessment of success is based on student portfolios and mid-term as well as final examinations.
17.ReadingforSpecificPurposes(IGS60205)
Reading for Specific Purposes course develops competencies dealt with in Basic Reading (getting general and specific information from the text, getting the main ideas and detailed information from the text, deducing the meaning of words, phrases and sentences based on the context, and explaining relations between parts of the text through grammatical cohesive devices, and developing the skills of inferencing, analysing, synthesizing, and speed reading), with the vocabulary mastery up to 6000 words and relevant grammatical structures used. This course also aims at developing the skills of text evaluation or reading critically. The use of full-scale texts of general topics should be encouraged and simplified texts should be avoided. Other than those given in Basic Reading, text types in Reading for Specific Purposes may include Explanation, Hortatory Exposition, Discussion. Analytical Exposition, Discussion, and Review. While individual performances are noted, pair and group work should be encouraged. Assessment of success is based on portfolios and mid-term as well as final examination.
18.AcademicReading(IGS60206)
This course aims to provide students with reading strategies for academic purposes. The approach draws on the concepts of genre-based reading as inspired by Systemic Functional Linguistic. Through interactive view which combines bottom up and top-down processing of reading, students are expected to be able to operationalize the reading concepts of skimming, scanning, inferencingandguessingmeaningfromcontextforacademicpurposes which requires efficient in time and effective in result. Class activities include understanding the three models of reading and the application of the models for academic reading. Discipline, integrity, and honesty are among affective aspects emphasized in this course.
19.InteractionalConversation(IGS60207)
This course is aimed at developing the students' English-speaking skill and competence in engagingindaily conversationsfreely, confidently,andfluently throughtopicsandactivities based on basic communicative competence. Topics to be covered are casual daily conversations, especially the basic language functions. Besides some lectures, the activities cover mostly speaking practices such as games, role play, quizzes, interviews, information transfer as well as information exchange. The evaluation on the students' achievement is based on the students' speaking performance in the classroom activities, in the mid test, as well as in the final test, and their classroom attendance as well as participation. The assessment criteria of the students' speaking performance are confidence, fluency, and appropriateness.
20.InstitutionalTalk(IGS60208)
This course is aimed at developing the students’ English-speaking skill and competence in engaging in formal conversations. The focus is on fluency, accuracy, and appropriateness. Topics to be covered are formal daily conversations in more complex themes. In addition to some lectures, the activities cover mostly speaking practices, such as games, role play, quizzes, interviews, information transfer as well as information exchange. The topics cover telephoning, giving opinion, conducting and reporting interview, reporting news, etc. The evaluation on the students’ achievement is based on the students’ speaking performance in the classroom activities, in the mid test, as well as in the final test, and their classroom attendance as well as participation. The assessment criteria of the students’ speaking performances are accuracy, fluency, and appropriateness.
21.PublicandAcademicSpeaking(IGS60209)
This course is aimed at developing the students’ skill and competence in expressing their ideas, thoughts, and feelings in more formal ways in various public speaking activities in non-academic settings. Fluency, accuracy, communicativeness, and appropriatenessshould be focused on. The topics include delivering speeches, chairing a meeting, conducting discussions, reporting, mc-ing, guiding, interviewing, debating, etc. The activities cover mostly speaking practices, some lectures and discussions. The evaluation on the students’ achievement is based on the students’ speaking performance in the classroom activities, in the mid test, as well as in the final test, and their classroom attendance as well as participation. Theassessmentcriteriaofthestudents’speakingability areaccuracy,fluency, appropriateness, eligibility, and performance.
22.IntermediateStructure(IGS60210)
As seen in the exercises provided, this unit is meant especially for Indonesian learners of English who have reached the intermediate level of English. The topics to highlight cover (1) the definition and classification of nouns according to their kinds, grammatical distinction, number, gender, and case, (2) noun phrase and compound nouns, (3) the definition and use of definite and indefinite articles, (4) pronouns, (5) concord between subjects and verbs, (6) verbs and verb phrases, (7) adjective and adverb, (8) adjective and adverb phrases. However, note to be considered that, since a clause has not been addressed in this unit, relative and interrogative pronouns, and a noun phrase of which structureismadeupfromaheadwordandadjective clausearenot included. Anounphrase with more complex modifiers will not be discussed in this unit, either. Whereas the course is in progress, students are introduced to English punctuation and spelling which are given in dispersal consistent with any topics related.
23.UpperIntermediateStructure(IGS60211)
This unit deals with upper intermediate structure of English by highlighting (1) the word order in noun phrases, (2) question tags and inversion with negative statements ( hardly ever, never, seldom and rarely, not only, etc), (3) to-infinitive and gerund, (4) auxiliary verbs (‘can/could’ and their differences from ‘be able to’ and ‘managed to’, ‘used to’, ‘must’, ‘have to’, and ‘need’), (5) adjective clauses and reduced adjective clauses, (6) adverb clauses and reduced adverb clauses, (7) noun clauses, (8) The Simple Present & Past Tenses, & (9) The Present and Past Continuous Tenses.
24.AdvancedStructure(IGS60212)
This course deals with pre-advanced structure of English by highlighting complex tenses like (1) the future tenses using the ‘will+ V1’ & the ‘be+going to+V1’ construction, (2) the present & past perfect simple & perfect continuous, (3) the future perfect & future continuous tenses, (4) the passive voices, (5) the active and passive causative, (6) the conditional sentences, (7) the subjunctive, (8) the inverted subject—verb, (9) Types of Sentences, and (10) Positive, Comparative, and Superlative Adjectives.
25.ParagraphWriting(IGS60213)
This course giveslearning experiences to develop fundamentalwritingskills at the sentence and paragraph levels. Classroom activities are focused on discussing grammatical accuracy and writing mechanics (spelling, punctuation, and capitalization) and developing writing strategies; outside classroom activities include writing paragraphs of good and correct English using appropriate vocabulary, simple organization, basic transitions, and various expository modes to achieve sentence coherence. Students are required to produce paragraphs on various topics consisting of 200-250 words during the course. Students are also expected to demonstrate a strong sense of discipline and responsibility, morals and ethics through the topic areas in the paragraphs they create. The topics may include personal descriptions, hobbies, travel, likes and dislikes, recipes, etc. Evaluation is based on the sum of scores on the individual writing assignments, mid-semester, and final tests.
26.EssayWriting(IGS60214)
This course focuses in developing a critical understanding of some key practices and examples of essay writing and the multiple kinds of work the essays do, such as commentary, social critique, and memoir. Also, this course is aimed to develop awareness of different rhetorical approaches used in essay writing. The goal of the course is oriented on how to produce essays that display clarity of purpose, awareness of audience, and sensitivity of writing mechanics and grammar. Course activities are including weekly paper and presentation, mid-term test and final test. Students are also required to submit one long essay concerning a certain topic in the end of the course. Assessment is based on regular attendance, papers, grades, and personal attitude in attending the course. Critical thinking, sensitivity towards social phenomena, creativity, discipline, and honesty are among skills and attitudes which are to be developed by this course.
27.AcademicWriting(IGS60215)
This course focuses on the writing process of organized academic essays containing introductions, body paragraphs, andconclusions, by developingwritingstrategiesandusing grammatically correct English to achieve unity and coherence. Students learn the principles of academic writing through modeling (observing and imitating), inquiry (answering questions and solving problems based on facts and observations), and discovery (finding concepts through aseries of data obtained throughobservation). The students are required to practicewritingessays duringthecourseby developingtheirskillsofwritingandavoiding plagiarism. Students are also expected to be able to build their critical thinking and cultural awareness and to demonstrate a strong sense of discipline and responsibility, morals and ethics in the essays they create. Assessment of success is based on the sum of scores on the individual writing assignments, mid-term project, and final project.
28.InterculturalCommunication(IGS60216)
This course explores the basic elements of interpersonal communication and culture as the two relateto oneanother. Emphasisisgivento theinfluenceofcultureontheinterpretation of the communication act and to the communication skills that enhance intercultural communication.
29.Pronunciation(IGS60217)
This course provides the students with practical skills and theoretical bases in pronouncing English words, phrases, and sentences in dialogues and passages. It consists of an 80% practical component and a 20% theoretical one. The practical component focuses on students’practiceofpronouncingindividualwords,phrases, andsentencesindialoguesand passages, with the lecturer giving the model pronunciation and providing supervision and feedback. The production of sounds is emphasized when pronouncing words, stress patterns when pronouncing phrases, and intonations when pronouncing sentences. The theoretical component deals with basic concepts of the English sound system and how the sounds are transcribed phonetically. Students have a lot of practices in transcribing words, phrases, and sentences in either dialogues or passages. The evaluation will be based on assignments, midterm test, final tests and class participation.
30.IntroductiontoEnglishLiterature(IGS60218)
This course provides students with knowledge and opportunity to examine the basic concepts and three principal genres of (English) literature. The materials are delivered throughlectures, classandgroupdiscussion, individualwork,andgroupassignments. Upon completion of this coursestudents are expected to possess a good understanding ofliterary works ranging from drama, novel, and poetry, and skills in analyzing them, and also a good attitude towards them. This course gives the students foundations of analyzing literary works and how to appreciate them. The topic includes literary work genres and their characteristics, basic literary theories, analysis and interpretation of literary works.
31.IntroductiontoLinguistics(IGS60219)
This course introduces students to the organization of language, the nature of language and the fields of Linguistics studies. Upon the completion of the course, students will possess good understanding about linguistic knowledge and the ability to analyze language structure based on various views of language. Topics include linguistics as scientific study of language, characteristics of language, theories of language, language change, phonological analysis, morphological analysis, syntactic analysis, semantic analysis, traditional grammar, transformational grammar, functional grammar, and pragmatics. Activities include lectures, discussions, presentation and individual or group work. Assessment is based on participation in class activities, assignments as well as final semester examination.
32.IntroductiontoTranslationStudies(IGS60220)
This course is designed to provide students with an introduction to the basic concepts of translation theory. Students will learn to develop an awareness of different perspectives of translation as well as a rational approach to translation in their own practice. Major issues in or related to translation are identified and discussed with reference to different conceptual frameworks. Students in group are given a topic to present in the class and attend lectures, and participate in class discussions to explore various aspects of this interdisciplinary area of inquiry.
33.CriticalTheory(IGS60221)
This course explores a range of theoretical ideas and concepts that have shaped literary studies today. This course will focus on the critical social theory of the “Frankfurt School” and its subsequent development. Building on the work of Marx, Freud and Lukács, the critical theory of the Frankfurt School was conceived in the 1920s as a research program that aimed to explain the persistence of social unfreedom in modern societies by drawing on insights from ideology theory, cultural theory, psychoanalysis and philosophy. Its main representatives, Max Horkheimer, Theodor W. Adorno, and Jurgen Habermas subsequently developed a radical philosophical critique of modern society and modern thought which they see as fundamentally determined by an imperative of domination which encompasses social and personal relations as well as the relation of humans to nature. The course will focus on getting an understanding of the main claims of historical and contemporary critical theories, on their normative impact on our contemporary thinking about justice and the good life and on whether they can contribute insights to current debates in philosophy. Students will find examples from literature and popular culture used to illuminate ideas and to show how theoretical concepts can open up possibilities in students’ reading and writing. To get a good understanding, students are to work in groups, presenting and discussing related materials; and, to work on individual paper projects. Assessment for this course is by group paper, group presentation, mid semester examination and final examination.
34.Lexico-grammar(IGS60222)
Uponcompletionofthiscourse, thestudentsareexpected to possessagoodunderstanding of word formation and sentence construction and skills for analyzing them. This course provides the students with theories and practices on English word formations and English sentence constructions from the perspective of systemic functional grammar. In terms of word formations, the topics include terms in morphology and morphological processes. In terms of sentence constructions, the topics include constructions of English phrases and clauses, includingtheirtypes. Thematerialsaredeliveredthroughlecturing, discussion, and group work. The students’ achievement is assessed on the basis of the participation in class activities, individual assignments, and the mid- and final-semester tests.
35.LinguisticApproachtoTranslation(IGS60223)
This course aims to provide students with a linguistic approach to translation. The approach drawsontheconceptsofSystemicFunctionalLinguisticforcontrastive-linguisticdescription to reveal the divergences and commonalities in the system and text between English and Bahasa Indonesia for translation purposes. Through the concepts of metafunction, stratification, axis, rank and delicacy students are expected to be able to translate texts from English into Bahasa Indonesia. Class activities include understading the five concepts and applying them as contrastive-linguistic description for translation purposes using descriptive data or real texts. Discipline, integrity, and honesty are among affective aspects emphasized in this course.
36.PhoneticsandPhonology(IGS60224)
This course is aimed at maintaining a good pronunciation of English. In general, it covers all aspects of speech sounds, their production and organization. Topics on phonetics will focus mainly on the articulatory phonetics together with some introduction to acoustic and perceptual phonetics. Phonology will start with the segmental and supra-segmental phonologies. It will also introduce some contemporary theories on phonology. Assessment is based on the mid and final examinations as well as final individual or group paper.
37.IntroductiontoChildren’sLiterature(IGS60225)
This course aims at introducing students with the genre of children’s literature and the urgent need to do an academic study on this area. The discussions will be focused on the genre of children’s literature, the essential elements of children’s literature and the understanding on children both as readers and text characters.
38.IntroductiontoDiscourseAnalysis(IGS60226)
Discourse Analysis (DA) is an interdisciplinary branch of linguistics which investigates any stretches/forms of language beyond the sentence level (in both spoken and written communication). This course offers an overview of several of the major theoretical and methodological frameworks for doing discourse analysis, and we will particularly give more attention to Multimodal Discourse Analysis (MMDA) and Critical Discourse Analysis (CDA). With the presentation and discussion of each approach, students will have the opportunity to try out different methods for the analysis of discourse using the different theoretical perspectives and methodologies. In doing such analyses of written and spoken language, students will try to make arguments for particular interpretations of the language they analyze using the appropriate terminology and methods to allow the data to support their argument. Discourse lends itself to a multi-teaching strategy that combineslecturing, group discussions and seminars, field work/research projects, corpus-based tasks, etc. Different methods of assessment are adopted, combining test(s), written/spoken assignments, and project work.
39.LiteraryTheories(IGS60301)
This course gives basic understanding and principles of most common literary theories as a foundation/spectacle of producing literary interpretation and analysis. In this course, the basic concept of some literary theories known today i.e. Moral Criticism, Biographical/Historical Criticism, New Criticism, Reader Response, Psychoanalysis, Feminism, Ecocriticism is introduced and discussed for a better understanding. The discussion will lead to the application of each theory in literary analysis. Upon completing this course, the students are expected to be able to use appropriate perspective in reading and analyzing a literary text.
40.SemanticsandPragmatics(IGS60227)
Semantics & Pragmatics is a two-credit compulsory subject. It provides an introductory study on meaning in language, both literal meaning and meaning constructed in relation to the users. It deals with the choices people make, the constraints they encounter in using languageinsocialinteractions, andtheeffectsoftheiruseoflanguageonotherparticipants in a speech event. Some topics to discuss are proposition, reference, deixis, lexical relation, participant role, implicature, presupposition, speech act, discourse structure, and politeness. During the course, students are presented with cases pertinent to the topics and analyze the cases in prescribed ways. At the end of the course students will achieve a competency in conducting studies on meaning in language, indicated by an awareness of the various aspects of meaning in language and an experience and ability in analyzing meaning in verbal communication.
41.Stylistics(IGS60228)
This course provides students with background knowledge about literary style, or the use of language in literature. The discussion is on general characteristic of language as a medium of expressions. It is the study of language as complement and aid to the study of literature. By learning these subject students are expected to have a new insight into language literature problems and to be able to recognize various characteristics ofliterature as a genre and of the style of individual authors. The materials are delivered through lectures, class and group discussion, individual work and group assignments.
42. TranslatingPractice(IGS60229)
Translating Practice is a two-credit point course and a prerequisite course to Translation Studies Concentration Program, with a C grade at the lowest. It aims at providing exposure for students about the practice of translating from English into Bahasa Indonesia. Students taking the course will be introduced to the relation between different language systems of English and Indonesia, looking at some linguistic features that are typically to do with system and text relations. The focus is to find out commonality and differences between thetwo languages. Assessmentforthecourseisbasedonregularassignments, discussions, special assignments or mid-semester and semester examinations.
43. IntroductiontoFilmStudies(IGS60230)
Introduction to Film Studies is a course designed to introduce students to the critical analysis of film as a literary text, art form, cultural product, and mode of communication. Through the study of selected films from various genres, periods, and regions, students learn to recognize and interpret the basic elements of cinematic language, including narrative structure, cinematography, editing, sound, and mise-en scène. This course equips students with greater awareness and critical insight when watching movies. Emphasis is placed on understanding the story to discuss the film, understanding how meaning is constructed through visual and aural techniques, and beginning to think about the social, cultural, and historical contexts in which films are made and received.
44.Showcase(IGS60231)
Showcase is one semester productive process in which, in the end, the students are encouraged to present the projects or research done during their study in a clear and creative way to audience. The learning outcomes will be presented in the so-called annual eventfeaturingtalks, poster, andcompetitions. Thetalks willbeintheformofthree-minute talks and the posters will be displayed in such a brief yet interesting and communicative way. Top presentations and posters receive awards at the conclusion of the event. The benefits that students can obtain from participating in the course are gaining experience presentingtheirideas, developingpublicspeakingorcommunicationskills, gettingfeedback from other students and lecturers, learning about research from peers, and competing for awards. The evaluation will be based on the products and presentations in the written and oral forms.
45.Children'sLiteratureCriticism(IGS60232)
This course aims at broadening as well as sharpening the students’ understanding on some important issues in the study of children’s literature such as pleasure, values, ideology, empowerment, agency, trust, control and censorship, multiculturalism and diversity. Each topic will be discussed in terms of the what, why and how they are important to address in thecontextofchildren’sliterature. Somechildren’stextsincludingfiction, nonfiction, picture books, graphic novels, poetry, films of different genres and formats will be used to sharpen the students’ understanding.
46.DramaAnalysis(IGS60302)
This two-credit introductory subject is intended to provide students with preliminary knowledge of drama and to train students with basic skills on analyzing drama. Focus of the study is directed to the achievement of literary competence related to the topic. The sub genres of drama, the elements of drama, and how to analyze drama focusing on each elementarebroadly discussed. Extensive andintensive readingonrelatedtopicsisassigned to the students. Students should read and analyze four plays and present their own papers on classroom discussion. Most topics are conducted through classroom discussion. At the end of the semester, students should write complete analyses on a drama.
47.LiteraryCriticism(IGS60233)
This 2-credit hour course is designed to introduce the students to the basic concepts of some contemporary literary theories after the “collapse of the paradigm” and to put them into practical criticism. The main objectives of this course are to make the students have 1) a critical awareness on the most contemporary literary theories, 2) the ability to generate and articulate their critical response to literary texts, and 3) the ability to produce critical literary analysis based on literary theories under study. Along the semester the students will be encouraged to discuss and produce critical literary analysis in the form of essays or research paper outline.
48.PoetryAnalysis(IGS60303)
The objective of Poetry Analysis courses is to outline the features in the growth of British, American, and Australian poetic traditions. The poems under analysis in this unit are those produced by British, American, and Australian poets by focusing on the major themes which may be regarded as significant concerning particular events in the development of the nations.
49.ProseAnalysis(IGS60304)
This course is aimed at making the students' literary reading habit more established by giving them a chance to read more British, American, Australian prose. At the same time their critical analysis should be improved by giving wider and deeper literary theories to apply in their reading and review production. about 6 short stories and 5 novels in a relatively higher degree of complexity will be assigned in this class.
50.StageProduction(IGS60234)
This course aims to explore the relationship between literature and theatre. The main focus of the course is the interaction between the literary skills of close reading, critical writing and discussion and the practical, aesthetic, and symbolic elements of performance. The course focuses on different aspects of literature and performance that cover the critical study of literary texts, the exploration of chosen approaches to a text, and the realization of texts in performances. Assessments cover students' progress report and final performance.
51.FilmCriticism(IGS60235)
Film Criticism is an advanced course that offers students the opportunity to engage deeply with cinema through critical analysis, theoretical frameworks, and cultural discourse. The course explores a diverse range of films from different genres and eras, encouraging students to interrogate the aesthetic, ideological, and narrative elements of film. Through close observation, scholarly reading, and critical writing, students learn to articulate nuanced interpretations and evaluate films with a deep understanding of cinematic form, historical context, and cultural significance. Students become familiar with major schools of film theory, including formalism, psychoanalysis, feminism, postcolonialism, and auteur theory. Students develop the ability to apply the perspectives of these theories in written criticism. The course emphasizes independent thinking, research, and scholarly approaches to film as a cultural text.
52.ResearchProposalandSeminaronLiterature(IGS60401)
This four-credit course aims at guiding students to write a thesis proposal in literature and hold a seminar forum. While exposing some theoretical material, it lays its emphasis more on practical activities. Prior to the seminar presentation, the students are provided with skills to develop along the course which cover all details of thesis writing-mechanics like how to write a sound background, research questions, limitation of the problem, and the literature review as well as the method planned to employ. Advanced literary competence as well as advanced skills of analyzing, evaluating, judging and criticizing a literary work are learnt. Contemporary and modern literary criticism is extensively applied. Through the seminar the students are to present their completed thesis proposals. It is expected that the students can gain insight from the feedback given by other students and the lecturer to their seminar presentation in order to develop their proposal into a sound thesis.
53.ArtificialIntelligenceforLinguistics(IGS60236)
Artificialintelligence(AI)israpidly transformingourworldandredefiningourways ofliving, working, and communicating. It additionally creates new opportunities for language research and application. This course bridges the fields of AI and linguistics by familiarizing students with the application of AI to manage linguistic data, encompassing both text and speech, while also addressing the limitations, risks, and ethical concerns associated with this technology. Upon completion of this course, students will be able to explain fundamental linguistic theories and their significance to AI models, assess the advantages and drawbacks of AI systems in linguistic tasks, and analyze ethical considerations. The class activities will include lectures, group presentations, group projects, and case studies. Students’ performance will be measured based on their participation, quizzes, assignments, and group projects.
54.CorpusLinguistics(IGS60237)
This course provides students with a basic understanding of the field of computational linguistics, which is a broad field incorporating research and techniques for processing language with computers at all levels of linguistic structure. Topics of discussion include what corpuslinguistics is, its history, tools and methods, and some current research in the area. Students in this class are expected to have a background in either computer science or linguistics, but not necessarily both. Class activities include lectures, group discussions, and presentation. Evaluation is based on the performance in the class activities, completion of assignments, and final project.
55.LanguageandtheMedia(IGS60238)
This course is aimed at giving the students the experience of analyzing the characteristics of language used in media and examining how developments in media have affected, and been affected by, language. The topics covered within this course is the use of language in newspapers, magazines, radio, television, email, the Internet, text messaging, and other media and how culture, politics, and social life are reflected in the media. The materials are delivered through lecturing, presentation, discussion and individual or group work. The students’ achievement is assessed on the basis of the participation in class activities, individual or group assignments, mid-term as well as the final semester tests.
56.Psycholinguistics(IGS60305)
Psycholinguistics aims to provide students with basic concepts about psychological and verbal processes of the production and perception of language. The competence of these willenablestudentsto buildaframework oftheaspectsofpsycholinguistics. The acquisition of the mother tongue and the aspects as well as concepts concerned will also be discussed. The functions, segments, and operations of the brain in relation to language production and perception will be another aspect of discussion. Topics in relation to mental process of producing and perceiving utterances and language acquisition, however, will be basic and utmost importance in this course. Lecture activities cover paper presentations and discussions. Evaluationcoversamid-termtest, presentation, researchproject, andscientific article.
57.Sociolinguistics(IGS60306)
Sociolinguistics is part of linguistics courses which are introduced to develop linguistic awareness of the students, to give knowledge on language functions and how they influence the speakers, to develop the students’ understanding of language varieties in their own society as well as others, and to develop the student's abilities in interpreting other people’s use of languages. This course deals with the following topics: language and social class, language, and ethnic group, language, and gender, language and geography, ethnography of communication, etc. Materials are delivered through lecturing, presentation, discussion, and individual or group work. Students’ evaluation is based on their participation in class activities, assignments, group mini-project, mid-term tests as well as a final test.
58.TheoriesandSchoolsofLinguistics(IGS60307)
This course introduces some prominent and influential modern theories and schools of linguistics. It provides students with essential characteristics of each theory and general principles of how the theories may fit into the linguistic methodology. In general, it aims to develop students’ good understanding of the various linguistics theories so that they can explain the theories and apply them to analyze phenomena of languages relevant to their daily life. Specifically, the students are expected to be able to explain fields of studies in linguistics, concepts and scope of theoretical linguistics, and concepts and analysis in interdisciplinary/applied linguistics. The topics to discuss include fields of study in linguistics, comparative-historical linguistics, Saussure’s structural theory, the Descriptivists: Boas and Bloomfieldian theories, Post-Bloomfieldian theory, the Sapir-Whorf hypothesis, Hjelmslev’s prolegomena to a theory of language, Tagmemic theory, Prague School theory, Generative Phonology, London School and Firthian linguistics, Chomsky’s Transformational-Generative Grammar, and Systemic Functional Linguistics.
59.DiscourseAnalysis(IGS60239)
This course introduces students to the different interpretations of discourse across the social sciences. It explores the ways in which language varies according to subject area, social setting, communicative purpose and the social roles and identities of those involved. It examines the workings of various forms of speaking and writing - casual conversation, interviewsandinterrogations, publicspeaking, emailingandmobilephonetextingandmass media articles, to cite just some examples. Students will study the nature of meaning, how we usually convey more than we actually say or write, the role of politeness in verbal communication, the necessarily cooperative nature of most forms of communication, and what makes texts cohesive and coherent. Through class presentation, discussion, and project, students will particularly be working with text, that is, larger units of meaning than a clause or sentence.
60.ResearchProposalandSeminaronLinguistics(IGS60402)
The course is a four-credit course providing learning experiences in writing a research proposalinEnglishasanintegratedapplicationofallsubjectmattersinthepreviouswriting courses and linguistic studies in the previous semesters. Classroom activities consist of giving examples, discussing topics and grammatical mistakes, and discussing theories and techniques of good writing. Outside classroom activities in the forms of individual assignments are done as further application and follow-up activities in the forms of tutorial and consultation are provided due to particular linguistic topics and difficulties. In the middle of the semester, the students are expected to complete a research proposal that will be presented in a weekly seminar. Seminar topics include phonological, morphological, syntactical, semantic analyses as well as analyseson sociolinguistics, psycholinguistics, and other fields of linguistics. In the seminar, the students take turn as presenter, moderator, paper reviewer, and audience. Evaluation is based on the student’s writing from the viewpoints of its content, organization, mechanics, and grammatical features as well as paper presentation, seminar attendance and participation, and the reworked seminar paper.
61.AudiovisualTranslation(IGS60308)
AudiovisualTranslationisacompulsory unitintheTranslationStudiesCurriculumofEnglish Literature Study Program, with a credit point value of 3 points (3 CPs). It provides students withanS1 levelofpracticalbilingualinterpretingpractice(classwork orlab-work)invarious typesofaudiovisualtranslationactivities(subtitling, dubbing, voiceover)underappropriate supervision. Students are to provide a recorder for the result of their practice. Assessment for the unit is based on contribution or participation in discussions, regular assignments, presentations/performances and responding to questions or comments, and final project/group assignment.
62.Computer-AssistedTranslation(IGS60240)
This course of Computer-Assisted Translation is an obligatory subject in the Translation Studies Curriculum of English Literature Study Program, for those students choosing to focus on Translation Concentration, with a credit point value of 2 points (2 CPs). It provides students with an S1 level of both theory and practice with the assistance of computer or certain software in various types of translation activities under appropriate supervision. Assessment for the unit is based on regular assignments, works produced, presentations/performances and discussions, portfolios, including the mid-semester examination and final assignment.
63.InterpretingPractice(IGS60309)
Interpreting Practice is a compulsory unit in the Translation Studies Curriculum of English Literature Study Program, with a credit point value of 3 points (3 CPs). It provides students with an S1 level of practical bilingual interpreting practice (classwork or labwork) in various types of interpreting activities under appropriate supervision. Students are to provide a recorder for the result of their practice. Assessment for the unit is based on regular assignments, works produced, presentations/performances and discussions, portfolios, with or without mid-semester examination and/or final assignment.
64.LegalDocumentTranslation(IGS60310)
Legal Document Translation is a compulsory unit in the Translation Studies Curriculum of English. LiteratureStudy Program, withacredit pointvalueof3 points(3 SKS). Thissubject provides students theoretical and practical knowledge concerning the characteristics of legal documents, various types (contracts, patents, ID cards, formal speeches, certificates, financialreports, courtdecisions, etc.), andstrategiesoftranslatingthedocumentsfocusing of the accuracy, legality, and confidentiality with no biases, false equivalents, personal interpretationorchangesinmeaning. Studentswilldo anS1 leveltranslationpracticeunder appropriate supervision. Assessment for the unit is based on contribution or participation in discussions, regular assignments, presentations/performances and responding to questions or comments, and final project/group assignment.
65.TranslationandMultimodality(IGS60241)
This course is designed to provide students with the basic concepts that multimodality is an inherent feature of all aspects of our lives and that meanings are realized through a great variety of symbolic modes. The verbal, aural and visual modes are seamlessly used for communication. As a result, the essential incommensurability between different modes in a text comes to the fore. This course is thus to get students exposed to the theory and practice of multimodal text translation in whichmeanings are not seen solely in each mode, but combined together for genuinely new meanings. Students in group are given a variety of multimodal text to analyze and discuss for case study and team-based project in the class.
66.TranslationCriticismandEvaluation(IGS60242)
This course aims to provide students with a perspective on translation criticism and evaluation. The perspective draws on the concepts and methods proposed by Julian House’s Translation Quality Assessment. Through the concepts of overt and covert translation, Ideology, Genre, Register, Discourse Semantics and Lexicogrammar are expected to be able to give criticism and evaluation to translated texts of Bahasa Indonesia - English. Class activities include understanding the six concepts and applying them as criticismandevaluationto translation. Discipline, integrity,andhonesty areamongaffective aspects emphasized in this course. After finishing this course, the students are able to.
67.LiteraryTranslation(IGS60243)
Literary translation is an elective unit in the Translation Studies Curricula of English Language and Literature Study Program and English Language Education Study Program, with a credit point value of 2 points (2 CPs). This course aims at introducing the students to theories and strategies of translating literary texts, including prose, poems, and drama. The materials cover analysis and discussions of other translation products; textual analysis and interpretation of the texts to produce aesthetic translations; and self-translating their literary writings. This course provides students with practices. Assessment is based on cognitive aspects, case studies, and team-based projects.
68.ResearchProposalandSeminaronTranslation(IGS60403)
The course is a four-credit course providing learning experiences in writing a research proposalin English as anintegrated application ofall subject matters in the previous writing courses and translation studies in the previous semesters. Classroom activities consist of giving examples, discussing topics and grammatical mistakes, and discussing theories and techniques of good writing. Outside classroom activities in the forms of individual assignments are done as further application and follow-up activities in the forms of tutorial and consultation are provided due to particular translation studies issues, topics and difficulties. Inthemiddleofthe semester, thestudentsareexpected to completea research proposal that will be presented in a weekly seminar. In the seminar, the students take turn as presenter, moderator, paper reviewer, and audience. Evaluation is based on the student’s writing from the viewpoints of its content, organization, mechanics, and grammatical features as well as paper presentation, seminar attendance and participation, and the reworked seminar paper.
69.Children’sLiteratureWriting(IGS60311)
In this course, students study the principles of writing for children, with emphasis on elements of craft, voice, form, and the reading and discussion of children’s literature. This course explores an extensive variety of children’sliterature including classic, contemporary, and multicultural titles across the genres. Students will understand the elements of and evaluation criteria for artistic and literary style in children’s literature. This course will familiarize students with major authors and illustrators and with award winning titles and authors/illustrators for the broadest base of the literature of childhood and give students a chance to compare and contrast different works, authors, and genres of children's literature. Students are to respond to children’s literature in a multitude of formats and to identity trends and issues in children’s literature and how they affect their future writing and publication. At the end of the semester, studnets are expeted to finish their writing on children’s literature. Assessment covers students’ progress report and final products.
70.ContentandCopywriting(IGS60404)
Both content and copywriting are used as digital marketing strategies and their roles are significantforbusinessinthisdigitalera. Whilewritingskillinthesetwo areasisparamount, other skills related to multimedia and the Web are needed to give immense effects on the reader. This four-credit course provides students with values, knowledge, understanding, and skills to develop their competence in content and copywriting. Topics in the course are organized based on the two areas, with content writing in the first half of the semester and copywriting in the second half of the semester. Instructional methods include lectures, discussion, discovery/independent and cooperative learning, and projects. Materials are delivered by the lecturers and practitioners, through face-to-face interactions in class and online mode. Students’ classroom activities include individual, pair, and group work, presentation, and discussion. The evaluation of students’ achievement is based on classroomparticipation, assignments, amid-semesterproject, anda final-semesterproject.
71.FictionWriting(IGS60312)
This course provides students with a solid grounding in the writing process, from finding inspirationto buildingabasicstory by usingliterarytechniquesandcreatingformsofprose. Students learn to develop a working knowledge of the basic elements of the craft of fiction: character, plot, point-of-view, dialogue, and setting. The students also practise the techniques to make the craft of fiction. By the end of this course, students are able to discover their creative thoughts and turn those ideas into pieces of creative writing. Assessment covers students’ active participation in class, completion of the assignments, and final writing.
72.JournalisticWriting(IGS60405)
The goal of this course is to build basic skills of newswriting and reporting so that students could report, conduct an interview, and write for mass-communication such as newspaper, magazine, radio, television. The topic areas of the course include news, features, and editorials. Students will be trained to maintain journalism ethics; independence, accuracy, impartiality, and truth, whenever they project or interpret an event for their publication. Thematerialsaredeliveredthroughlecture, discussion, workshopwithjournalistandmedia practitioners, individual project, and group assignments. At the end of the course, students are expected to have a good understanding on how a journalist works. Assessment covers students’ participation, weekly projects, and a final project.
73.KuliahKerjaNyata(KKN)(MLK60605)
Mata kuliah ini menyiapkan mahasiswa untuk dapat mengimplementasikan ilmu yang dipelajari sesuai bidang keilmuannya di lokasi KKN. Pembekalan yang diberikan sebelum mahasiswa diterjunkan ke lokasi KKN meliputi bidang kompetensi program studi dalam menghadapi berbagai permasalahan masyarakat di lokasi KKN. Mahasiswa diharapkan bisa berkolaborasi dengan berbagai kalangan dan mahasiswa dari berbagai program studi di UNY sehingga mahasiswa mampu melaksanakan program multidisiplin dalam menyelesaikan permasalahan di masyarakat.
74.PraktikKerjaLapangan(PKL)(MLK60604)
Magang merupakan upaya peningkatan pemahaman, wawasan, dan keterampilan mahasiswa sebagai calon Sarjana S1, sehingga semua mahasiswa Prodi Sastra Inggris wajibmengikutinya untuk melengkapikompetensiyangtelahdiperolehselamaperkuliahan. Praktik Kerja Lapangan atau magang/internship Prodi Sastra Inggris merupakan suatu penugasan bagi mahasiswa untuk melakukan pengamatan dan praktik bekerja di perusahaan/lembaga/instansi mitra prodi selama minimal 272 jam kerja atau 2 bulan fulltime (5 hari kerja per minggu dengan 7 jam kerja per hari) yang ekuivalen dengan 6 SKS lapangan. Program ini dilaksanakan secara reguler baik pada semester ganjil maupun genap (semester 7 dan 8). Sebelum mengikuti PKL, mahasiswa berkonsultasi dulu secara intensif dengan dosen pembimbing untuk menentukan lokasi, periode, dan job description yang akan dikerjakan. Penilaian dilakukansecara kolaboratif antara dosen pembimbing dan praktisi pembimbing di perusahaan/lembaga/instansi mitra dengan mempertimbangkan berbagai aspek seperti kelengkapan laporan kegiatan, produk yang dihasilkan, dan kinerja selama PKL.
75.MetodologiPenelitian(MKK60301)
This course provides background knowledge of how to conduct a research study on language and literature. Some important and general concepts in research methods are given to give good insight to the matter. Topics to discuss include, but not limited to, the nature and types of humanities and social science research, steps in conducting the research, the methods in collecting and analyzing the data, trustworthiness, et cetera.
76.TugasAkhir(MKK60801)
Thestudentsareable to 1. demonstratetheircompetenceinmasteringtheknowledge they concentrate on literature or linguistics or translation. 2. express the idea in writing expressions. 3. present the idea orally in front of the examiners.
77.EnglishforBusinessCommunication(IGS60301)
This course is designed to introduce students to English effectively used in business or business-related as well as to introduce them to some real practices of business discourse. Topics include events commonly found in the pre-employment texts and during employment texts. Added to this, the course will also provide students with model texts, essential grammar, and vocabulary in contexts. The activities include lecturing, business communication practices (speaking and writing tasks), and discussions. The evaluation will be based on assignments, midterm test, final test, and class participation.
78.HistoryofModernThoughts(IGS60202)
This course is planned to introduce students into the history of western philosophy, which is assumed as the fundamental system of ideas formulating modern civilization. It covers big philosophers, from the classics to the most contemporary era considered relevant to students’ necessity in comprehending the ideas of modernity. The emphases are on how the thinkers formulate philosophical questions, how they construct their ideas, how their ideas are interconnected with the history of philosophy, and what atmospheres surround the formulationof theirideas. To get a good understanding, students are to workin groups, presenting and discussing related materials; and, to work on individual paper projects. Assessment for this course is by group paper, group presentation, mid semester examination and final examination.
79.Kreatifitas,Inovasi,danKewirausahaan(IGS60203)
Mata kuliah ini bertujuan untuk mengembangkan kompetensi mahasiswa dalam berwirausaha, berkreasi dan inovasi. Pembelajarannya berorientasi pada teori dan praktik berusaha baik secara mandiri maupun kelompok. Selain itu, bentuk luaran yang diharapkan adalah proposal kewirausahaan dan inovasi teknologi Pendidikan dan layanan jasa. Perkuliahan diberikan secara daring melalui Besmart dan Zoom. Dengan diberikannya mata kuliah ini, mahasiswa diharapkan mampu merancang usaha, menjalankan usaha, membuat inovasi teknologi Pendidikan dan jasa untuk masyarakat. Materi disajikan dalam bentuk video, serta handouts. Penilaian pencapaian pembelajaran mahasiswa dilakukan melalui penugasan di luar kelas, quiz, dan UAS.
80.LiterasiDigital(IGS60201)
Literasi digital merupakan efek digitalisasi karena perkembangan teknologi yang mendorong perubahanpadaberbagaiaspekdimasyarakat.Literasidigitalmerupakanbagianakhirdaritahapan teknologidigitalyaitukompetensidigitaldanpenggunaandigital.Perkembanganteknologiyangpesat memunculkan tantangan dan peluang bagi pengguna dalam menyediakan teknologi terbaru untuk dapat menyesuaikan dengan perubahan yang ditimbulkan. Pengetahuan lintas bidang ilmu telah memunculkan inovasi-inovasi baru dengan memanfaatkan berbagai platform digital yang dapat menjadi media transfer data dan informasi dalam jumlah yang tak terbatas (big data). Konektivitas melaluiinternettelahmemperluasmanfaatdimanainformasidanpenggunayangtersambungsecara terusmenerus.
Tabel 23. Daftar Kode dan Nama Mata Kuliah Program Studi Sastra Inggris
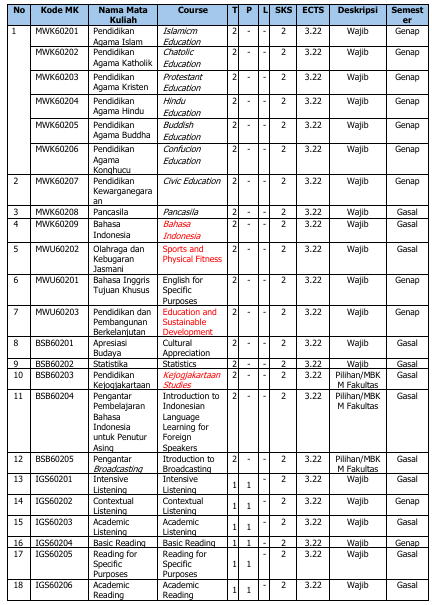


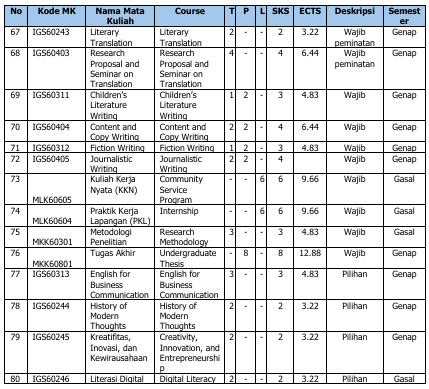
PENUTUP
KurikulumProgramStudiSastraInggristahun2025merupakanhasildariprosesevaluasi yang komprehensif, berbasis data, serta mempertimbangkan dinamika perkembangan ilmu pengetahuan, teknologi, dan kebutuhan masyarakat serta dunia kerja. Dengan mengusung pendekatan Outcome-Based Education (OBE), kurikulum ini tidak hanya menitikberatkan pada capaian akademik, tetapi juga menyiapkan lulusan yang adaptif, profesional, dan siap bersaing dalam skala nasional maupun internasional.
Kurikulum ini dirancang untuk mengembangkan kompetensi utama di bidang bahasa, sastra, dan penerjemahan yang diperkaya dengan nilai-nilai lokal dan global, literasi digital, serta keterampilan komunikasi profesional. Penerapan pembelajaran berbasis proyek dan pengalaman langsung melalui kegiatan magang dan kolaborasi eksternal diharapkan mampu menumbuhkan karakter lulusan yang kreatif, inovatif, dan berdaya saing tinggi.
Melalui kurikulum ini, Program Studi Sastra Inggris berkomitmen untuk terus memberikan pendidikan yang berkualitas, relevan dengan perkembangan zaman, serta selaras denganvisiuniversitassebagaiinstitusipendidikantinggiyangungguldanberdaya saingglobal. Kurikulum ini juga menjadi landasan strategis dalam menciptakan lulusan yang tidak hanya cakap secara akademik, tetapi jugamampumenjadi agen perubahan yang membawa kontribusi positif bagi masyarakat dan dunia keilmuan.
Contact Us
Copyright © 2026,
